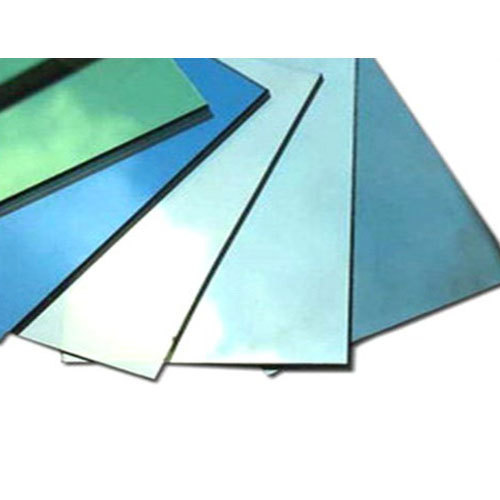
Coated Glass
Coated glass is a specialized type of glass that undergoes a process where thin layers of coatings or films are applied to enhance its performance and appearance. These coatings can serve various purposes, from improving energy efficiency to providing privacy and altering the aesthetic properties of the glass. Coated glass has become a staple in modern architecture, offering a versatile solution that meets diverse functional and design requirements.
Key Characteristics
Energy Efficiency: Coated glass often features low-emissivity (low-E) coatings that enhance energy efficiency by reducing heat transfer. This helps in maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures while minimizing the need for excessive heating or cooling.
Solar Control: Some coated glasses are designed to control solar radiation, preventing excessive heat gain and glare in interiors. These solar control coatings contribute to a more comfortable and visually pleasing environment.
Reflectivity: Coated glass can exhibit varying levels of reflectivity, providing architects and designers with options to achieve specific visual effects. Reflective coatings contribute to the aesthetics of a building's exterior while controlling light penetration.
Privacy and Security: Certain coated glasses offer enhanced privacy by creating one-way vision or by obscuring views from the outside. Additionally, security coatings can be applied to strengthen the glass, making it more resistant to breakage.
UV Protection: Coated glass can feature coatings that block a significant portion of ultraviolet (UV) radiation. This UV protection is essential in preventing the fading of interior furnishings and protecting occupants from harmful UV rays.
Common Uses of Coated Glass
Low-E Coated Windows
Solar Control Glass
Reflective Facades
One-Way Vision Partitions
Automotive Glazing
UV-Blocking Windows
Security Glass
Greenhouses
Mirrored Surfaces
Electronic Displays
Send enquiry Pay Online
Pay Online